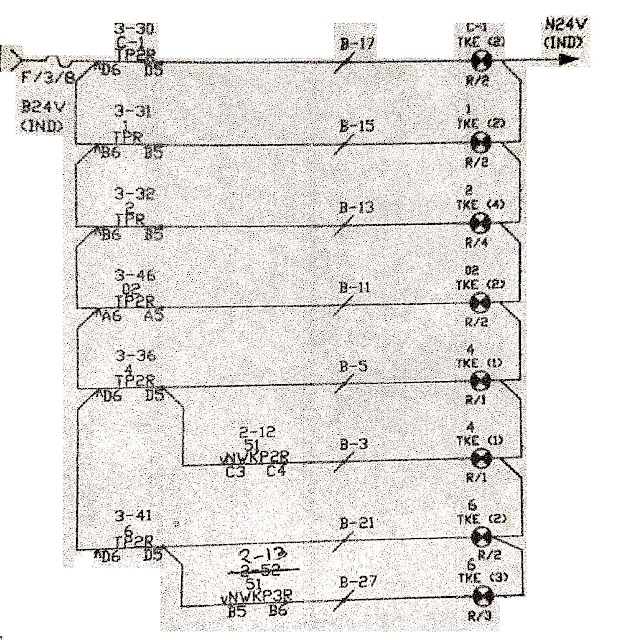
LAMP CHECKING RELAYS (ECRs) ->
- DECR
- HECR
- RECR
- UECR
- SHUNT ON ECR
- SHUNT OFF ECR.
- CALLING ON ECR.
- PROCEED ASPECT LAMP CHECKING RELAY(DECR)
- To understand DECR first take Yard diagram .
Lets take OFF signals for run through for Main line.
Thereby S1DR, S1HR picks up. Through the picks up contact of S1DR, S1HR, its repeaters S1DPR, S1HPR picks up at signal location.
An 110V AC is applied to S1DG lamp through S1-DECR coil, HR, DR and DPR front contacts.
Thereby S1DG lamp glows and the DECR relay picks up. Through DECR front contact, a green indication is provided in the S1 signal aspect on the panel.
Suppose S1DG Lamp fail to glow , then cascading circuit will work.
Means through S1DECR back contact , S1HG(Yellow aspect) will glow and S1HECR is picked up.
Suppose S1HG Lamp fail to glow , then cascading circuit will work.
Means through S1HECR back contact and S1HG front contact ,the supply is applied to S1RG(Red aspect) will glow and S1RECR is picked up.
2. Caution Aspect Checking Lamp (HECR) Circuit.
- Default S1 RG aspect will be glowing.
Suppost S1 signal is taken Off for Loop Line, its caution aspect controlling relay (HR) pickup contact ,thereby the caution aspect repeater /proving relay (HPR) at signal location picks up .
Through the pickup contact of S1HR , S1HPR, back contact of S1DECR and S1HECR coil, 110VAC is applied to S1HG Lamp.
Thereby S1HECR picksup and corresponding circuit indication is provided in the signal aspect on the panel.
Suppose S1HG fails to glow, then cascading arrangement enable the S1RG lamp to glow.
3) ON aspect lamp Checking Relay (RECR) circuit.
When a signal is not taken OFF , Through the back contact of HR and RECR coil , the supply is extended to S1RG.

The S1RG lamp glows thereby S1RECR is pickup , the corresponding indication is provided in the signal aspect on the panel.
4) Route Lamp Checking Relay (UECR) circuit.
When Home signal S1 is taken OFF for the Loop line, then the signal control relay for route (S1UGR) picks up in the relay room, which energises its repeater S1UGPR at signal location box.

The 110 AC Volt is applied in parallel to S1 route lamp (5 Numbers) through the front contact of S1UGPR and S1UECR coil.
When Minimum three lamps are burning in the route , then S1UECR picks up.
Through the S1UECR front contact , S1UECPR is picked up at the relay room and the corresponding route indication is provided on S1 signal on the panel.
For picking up UECR minimum 3 lamps out of 5 should glow in the route.
5) SHUNT ON ECR:(In Independent Shunt Signal)
When a signal is not taken OFF , the SH201 HR will be in dropped condition .
Through the SH201 HR back up contacts and SH201 ON ECR coil, the supply is extended to SH 201ON aspect lamp and SH 201 pilot lamp.
When the Both lamp burn , the SH 201 ON ECR is picked up and the corresponding indications are provided on the SH 201 signal on the panel.

5) SHUNT OFF ECR
Through SH201 HR , SH201 HPR front contact and SH201 OFF ECR coil, the supply extended to SH201 OFF aspect lamp and it burns.
Through HR front contact and SH 201 OFF ECR coil, the supply is extended to SH 201 pilot lamp and its burns.
Then SH 201 OFF ECR is picked up and the corresponding indications are provided on the SH201 signal on the panel.
- Default S1 RG aspect will be glowing.
Suppost S1 signal is taken Off for Loop Line, its caution aspect controlling relay (HR) pickup contact ,thereby the caution aspect repeater /proving relay (HPR) at signal location picks up .
Through the pickup contact of S1HR , S1HPR, back contact of S1DECR and S1HECR coil, 110VAC is applied to S1HG Lamp.
Thereby S1HECR picksup and corresponding circuit indication is provided in the signal aspect on the panel.
Suppose S1HG fails to glow, then cascading arrangement enable the S1RG lamp to glow.
3) ON aspect lamp Checking Relay (RECR) circuit.
When a signal is not taken OFF , Through the back contact of HR and RECR coil , the supply is extended to S1RG.

The S1RG lamp glows thereby S1RECR is pickup , the corresponding indication is provided in the signal aspect on the panel.
4) Route Lamp Checking Relay (UECR) circuit.

The 110 AC Volt is applied in parallel to S1 route lamp (5 Numbers) through the front contact of S1UGPR and S1UECR coil.
When Minimum three lamps are burning in the route , then S1UECR picks up.
Through the S1UECR front contact , S1UECPR is picked up at the relay room and the corresponding route indication is provided on S1 signal on the panel.
For picking up UECR minimum 3 lamps out of 5 should glow in the route.
5) SHUNT ON ECR:(In Independent Shunt Signal)
When a signal is not taken OFF , the SH201 HR will be in dropped condition .
Through the SH201 HR back up contacts and SH201 ON ECR coil, the supply is extended to SH 201ON aspect lamp and SH 201 pilot lamp.

5) SHUNT OFF ECR
Through SH201 HR , SH201 HPR front contact and SH201 OFF ECR coil, the supply extended to SH201 OFF aspect lamp and it burns.
Through HR front contact and SH 201 OFF ECR coil, the supply is extended to SH 201 pilot lamp and its burns.
Then SH 201 OFF ECR is picked up and the corresponding indications are provided on the SH201 signal on the panel.